Vaginal Health
November 01, 2024
5 min read
Yeast Infections vs. Bacterial Vaginosis: The Differences, Similarities, and Natural Solutions
Not sure which vaginal infection you have? Here’s how to spot the differences and choose the best natural treatments for BV and yeast infections.

Gut Health
August 19, 2024
4 min read
Gut Health & Aging: Why Probiotics Are Important As You Get Older
How a nutritious diet and high-quality probiotic supplement can help you avoid infection and illness as you age.

Vaginal Health
Boric Acid for Yeast Infections: An All-Natural Way to Boost Vaginal Health
Discover the best boric acid suppository for treating yeast infections naturally and improving vaginal health.

Gut Health
UTIs
Vaginal Health
April 25, 2024
4 min read
The Gut-Vagina Connection: How to Boost Vaginal Health Through a Balanced Gut
A healthy gut can help prevent yeast infections, bacterial vaginosis, UTIs, and other vaginal conditions—all while balancing the vaginal flora.

Overactive Bladder
video
April 04, 2024
0 min read
Bladder Health Explanatory Video
Learn how Utiva Bladder Health can help manage mild to moderate overactive bladder (OAB) symptoms. It uses a proprietary formula (Flowens) which is clinically proven to help strengthen urinary function for men and women such as bladder emptying, urinary frequency, and flow.

Vaginal Health
March 28, 2024
5 min read
Vaginal pH 101: A Balancing Act
Learn how the vaginal pH works and how to keep it balanced with a yeast infection treatment like a boric acid suppository.

UTIs
Vaginal Health
February 05, 2024
4 min read
How Do I Know if I Have a Yeast Infection, a UTI, or Something Else?
Many vaginal conditions have similar symptoms, like yeast infections and urinary tract infections. Here’s how to tell the difference.

Overactive Bladder
January 09, 2024
5 min read
Can You Treat Overactive Bladder Naturally?
Discover the many treatment options for overactive bladder, including lifestyle modifications, prescription drugs, and supplements to treat OAB naturally.

video
December 29, 2023
0 min read
Cranberry PACs Explanatory Video
Learn how cranberry PACs work to naturally prevent urinary tract infections (UTIs). Utiva provides 36mg of cranberry PACs (active molecules) in each capsule measured scientifically by DMAC/A2 to ensure the best quality for urinary tract health.

UTIs
December 11, 2023
1 min read
What are silent UTIs?
Recent studies have shown that “normal” urine may be colonized with many different micro-organisms that do not necessarily cause harm.

UTIs
Vaginal Health
October 30, 2023
4 min read
Vaginas and UTIs: Understanding the Vaginal Microbiome and its Impact on Your Urinary Health
The healthier your vagina is, the less likely you are to get UTIs. Here’s everything you need to know.

Overactive Bladder
UTIs
October 24, 2023
2 min read
Breaking down doctor language: How to decode what your doctor is saying?
Here are some common terms used by doctors in the world of urinary tract health.

UTIs
September 04, 2023
3 min read
The Link Between Dementia and UTIs: Spotting the Signs and Preventing Infection
People with dementia are twice as likely to develop UTIs. Here’s how to spot the symptoms and prevent infections, including the best cranberry pills for UTI.

UTIs
August 22, 2023
1 min read
If you get a UTI, does that mean you will have another one?
Although it's common to have a UTI more than once in your life, having one UTI does not condemn you to multiple UTIs to come!

UTIs
How to Establish Healthy Habits (And Stick to Them)
A full guide to breaking habits, forming healthy ones, and using them to improve your well-being—from your mental health to your urinary tract.

Overactive Bladder
UTIs
Vaginal Health
Pelvic Health Issues in Women: Navigating Challenges at Every Age
UTIs from sex. Bladder problems postmenopause. Women are prone to pelvic health issues at every age—but prevention is possible through lifestyle changes and supplements.

UTIs
Vaginal Health
Yeast infection vs. UTI: How can you tell the difference?
Sometimes telling the difference between a yeast infection and UTI can be tricky. Here are some key differences to look out for.

UTIs
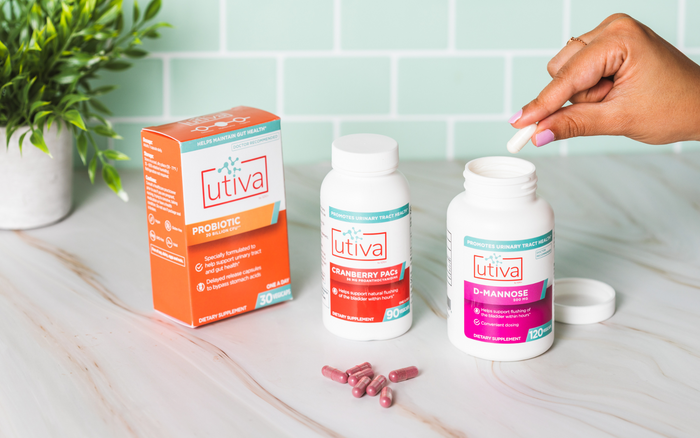
Natural Supplements for UTI Prevention
Utiva cranberry pills, D-mannose, and probiotics are all high-quality natural supplements for UTI prevention.
UTIs
April 18, 2023
5 min read
Biofilms: The Not-So-Secret Cause of Chronic UTIs
Suffering from frequent UTIs? Biofilms might be to blame. Here’s how to prevent them, including the best cranberry pills for UTIs.

UTIs
April 11, 2023
2 min read
Flowens vs. PACs: What is the difference?
Clearing the confusion on how Flowens and PACs provide different benefits for urinary tract health (even though both are technically cranberry).

Overactive Bladder
March 13, 2023
3 min read
Lifestyle changes and herbal options for OAB. What can you do on your own?
Urologist, Dr. Yana Barbalat explains 5 ways you can naturally manage OAB symptoms on your own, before seeing a doctor – aka first-line treatment for OAB.

Gut Health
UTIs
March 06, 2023
4 min read
Why should you take a probiotic with Lactobacillus to prevent UTIs?
Do probiotics help UTI prevention? The answer is yes—as long as they contain Lactobacillus. Discover the benefits of this superstar bacteria for UTI prevention, immune function, gut health, and more.

Gut Health
UTIs
February 22, 2023
7 min read
9 signs of an unhealthy gut (and what to do about it)
Your gut microbiome is the foundation of your health. Here are 9 signs that it needs some love—plus our top tips for boosting your gut health over time.

UTIs
February 15, 2023
6 min read
How to optimize water intake for better bladder health
Drinking more water is crucial for staying healthy and preventing UTIs. Here are tips to stay hydrated and boost water absorption.

UTIs
January 30, 2023
2 min read
Is it possible for a UTI to go away without the use of antibiotics?
Good news - for some UTI patients, all it takes is waiting 48 hours to feel better. That's why its usually recommended to hold off on antibiotic treatment unless symptoms worsen.

UTIs
January 17, 2023
4 min read
3 incredible health benefits of D-mannose
Meet D-mannose: an all-natural sugar that can prevent UTIs, stimulate good bacteria growth, and even treat a rare disease called carbohydrate-deficient glycoprotein syndrome type 1b.

Overactive Bladder
January 11, 2023
3 min read
The 411 on Incontinence
Most people think that all incontinence is the same, but incontinence comes in few different varieties: stress incontinence, urge incontinence, and overflow incontinence. Here is the difference between all three forms and how to treat them.

UTIs
December 06, 2022
5 min read
The amazing health benefits of cranberries: From UTI prevention to cancer
Cranberries can prevent UTIs, kill cancer cells, lower cholesterol, and even improve your memory. But how you consume them makes a difference. Here’s everything you need to know.

UTIs
November 21, 2022
5 min read
UTIs during pregnancy: Your guide to risks, treatment, and prevention
Over 30% of pregnant women will get a UTI. Here’s why it’s so common and how you can prevent UTIs during pregnancy—and beyond.

Prostate Health
November 09, 2022
5 min read
What is the best age to start taking care of your prostate?
50% of men over the age of 50 are impacted by their enlarged prostate. Here’s a guide for when (and how) to start taking action on your prostate health — from screening options to the best prostate supplement.

Overactive Bladder
UTIs
November 03, 2022
2 min read
If I am experiencing frequency, how can I tell if it’s from OAB or infection?
It's not easy to define urinary frequency because what’s “normal” is different for everyone, depending on fluid intake and many other factors. Urologist, Dr. Yana Barbalat explains some of the most common reasons why you might be experiencing frequency.

UTIs
October 12, 2022
2 min read
I am experiencing UTI symptoms, but my urine cultures keep coming back negative. What should I do?
Just because you feel like you have a UTI, doesn't always mean that you have a UTI. There are many causes of UTI like symptoms which are often very treatable. The key is to find a good doctor and get the right diagnosis.

Overactive Bladder
Prostate Health
September 20, 2022
2 min read
Can men get overactive bladder? How is it different from prostate issues?
OAB can be a confusing topic because there are many causes for both men and women, and research is still under way. Here is a list of what we know can cause OAB in men and how OAB differs from prostate issues.

UTIs
August 22, 2022
5 min read
The different types of cranberry measurements and why they matter for UTI supplements
How do you know if a cranberry supplement is effective? It all depends on the amount of PACs and how they’re measured.

UTIs
August 17, 2022
3 min read
What can family members do for seniors who have recurrent UTIs?
How you can recognize their symptoms and avoid antibiotic use when unnecessary? Understanding and managing a senior’s UTI symptoms can be tricky, but prevention is possible with the proper education and resources.

Overactive Bladder
August 15, 2022
5 min read
The side effects of OAB medication and how they impact patient compliance
78% of people who start OAB drugs stop taking them within a year. Here are the harsh side effects to watch out for, plus the natural OAB supplement that can help.

Overactive Bladder
August 15, 2022
6 min read
Most asked questions people have about overactive bladder
Struggling with OAB symptoms? Here are the answers to all of your burning questions.

UTIs
How much cranberry juice or dried cranberries will give you 36mg of PACs?
Cranberry juice has been studied for prevention of urinary tract infections and 240 – 300 ml of cranberry juice in those studies yielded 36-40 mg of PACs. However, this is something that cannot be generalized to all cranberry drinks and juices.

Overactive Bladder
UTIs
What is the recommended treatment of an elderly patient with incontinence and recurrent UTIs?
Incontinence and recurrent UTIs often co-exist in the same population of geriatric patients. Therefore, it can be tricky to figure out whether to treat a UTI based on the degree of incontinence.
UTIs
What is the official urologist protocol for treating a positive dip stick?
As a urology community, we have guidelines that can help guide our management but very often doctors differ in their practice based on their experience and training. There is also a constant influx of new data that can guide us one way or another.
UTIs
April 21, 2022
1 min read
Are cranberry pills safe for people who are on blood thinners?
Cranberries are considered safe for patients who take Warfarin (Coumadin®). All recent larger studies point to the fact that there is no interaction between cranberry and blood thinners. Therefore, experts believe that cranberries, and cranberry products, are safe to consume with Coumadin®.

UTIs
April 21, 2022
1 min read
Are cranberry pills safe for people who suffer from kidney stones?
Scientific evidence shows that the consumption of cranberry juice does NOT increase urinary oxalate levels or increase the risk of stone formation. In fact, studies have shown that cranberry juice may suppress kidney stone formation by LOWERING urinary oxalate excretion and increasing citrate excretion, which tends to prevent stone formation.

UTIs
April 21, 2022
1 min read
Is it Safe to Use D-mannose in patients with diabetes?
D-mannose is a sugar found naturally in many fruits and berries. However, unlike glucose, a sugar that we have all heard about, D-mannose is absorbed very slowly in the gut making it safe for people whith diabetes.

UTIs
April 14, 2022
7 min read
How to stay hydrated and prevent UTIs during Ramadan
During Ramadan, fasting can cause major dehydration and other complications, like UTIs. Here’s how to make this your healthiest, most hydrated Ramadan yet.

UTIs
Vaginal Health
April 07, 2022
6 min read
Let’s Talk: Taboos and Stigmas Around Women’s Health & UTIs
45% of women don’t talk to anyone about their vaginas. To smash the stigma, we need to talk openly about women’s health, from UTI treatment to sexual pleasure.
UTIs
March 28, 2022
1 min read
What is the role of ureaplasma in UTIs?
Ureaplasma is a bacterium that is sometimes found in the vagina. This bacterium typically comes from a current or previous sexual partner and lives in the vagina along with the other bacteria that co-exist in there, often not causing any symptoms or long-term issues.

UTIs
March 17, 2022
1 min read
Skene’s Glands and UTIs: What’s the deal?
Skene’s glands consists of two small ducts located along both sides of the female urethra. They are composed of the same tissue as the clitoris and play a vital role in both urinary and sexual health. Occasionally, when people have frequent urinary tract infections, the skene’s glands can get recurrently infected with bacteria and inflamed.

UTIs
March 07, 2022
3 min read
What are the most common UTI-related questions a urologist gets?
UTIs are very distressing and tend to really impact one’s quality of life. Some patients develop recurrent urinary tract infections and that’s generally when they get referred to a urologist. Doctor Yana Barbalat answers the most common UTI-related questions she gets.

UTIs
January 03, 2022
2 min read
How do I know the difference between Interstitial Cystitis and UTI?
A urinary tract infection (UTI) happens when bacteria adheres to the bladder wall and infects parts of the urinary tract. Interstitial cystitis (IC) is a painful bladder condition with an unknown cause. How can we tell the difference between the two? Board Certified Urologist, Yana Barbalat gives us her take on what sets these two conditions apart.

























































